CORIFACT Replaces Missing Coagulation Factor XIII
Administration of CORIFACT to patients with Factor XIII (FXIII) deficiency replaces the missing coagulation factor.
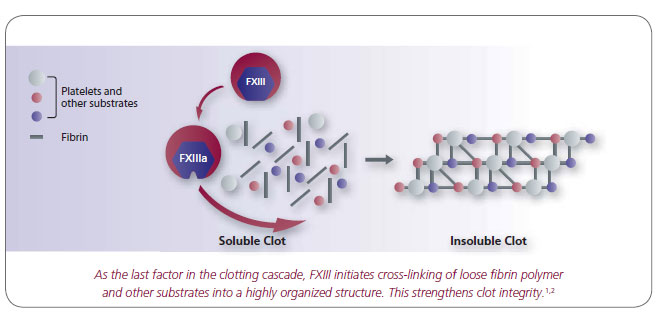
Factor XIIIa (activated form) is involved with: 2, 3
- Cross-linking of fibrin strands and other proteins during coagulation
- Formation of strong, stable clots that are firmly anchored to sites of blood vessel injury
- Protection of clots from fibrinolysis
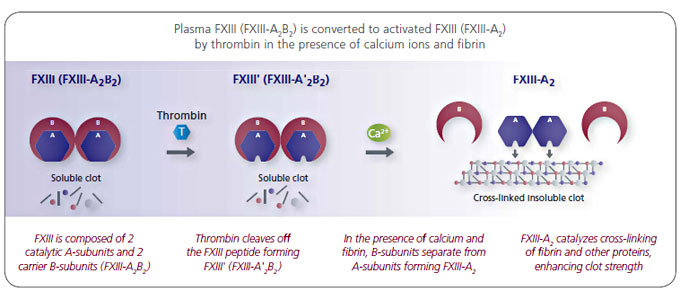
FXIII that is found in the body consists of 2 A-subunits and 2 B-subunits2
Both of these dual-subunits are required for normal FXIII function.4
- A-subunits are essential to the physiological protection of the clot against fibrinolysis: 2, 4
- Initiate cross-linking of fibrin and other proteins to help stabilize the clot
- Make the clot more elastic
- B-subunits act as carrier molecules, stabilizing the A-subunit: 2, 3
- Help prevent degradation of the A-subunits, prolonging their half-life
- Localize FXIII to the growing fibrin polymer to initiate the cross-linking process
- No enzymatic activity
Important Safety Information
CORIFACT®, FXIII Concentrate (Human), is indicated for routine prophylactic treatment and perioperative management of surgical bleeding in adult and pediatric patients with congenital Factor XIII deficiency. CORIFACT must be administered intravenously.
CORIFACT is contraindicated in individuals with known anaphylactic or severe systemic reactions to human plasma-derived products.
Hypersensitivity reactions may occur with CORIFACT. If there are signs of anaphylaxis or hypersensitivity reactions (including urticaria, rash, tightness of the chest, wheezing, and hypotension), immediately discontinue administration and institute appropriate treatment.
Inhibitory antibodies to FXIII have been detected in patients receiving CORIFACT. Monitor the patient’s trough FXIII activity level during treatment. If expected plasma FXIII activity levels are not attained or breakthrough bleeding occurs, perform an assay measuring FXIII inhibitory antibody concentrations.
Thromboembolic complications have been reported with CORIFACT; monitor patients with known risk factors for thrombotic events.
CORIFACT is derived from human blood. The risk of transmission of infectious agents, including viruses and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent and its variant (vCJD), cannot be completely eliminated.
The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials (frequency >1%) following treatment with CORIFACT were joint inflammation, hypersensitivity, rash, pruritus; hematoma, arthralgia, headache, elevated thrombin-anti-thrombin levels, and increased blood lactate dehydrogenase. Serious adverse reactions included hypersensitivity, acute ischemia, and neutralizing antibodies against FXIII.
Please see full prescribing information for CORIFACT.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact the CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance Department at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov/medwatch.